[인터페이스]
- 내가 만들어야 할 기능이 선언만 되어있는 것 (껍데기)
- 투두리스트 처럼 메소드 나열
[public] interface 인터페이스이름 { ... }
//예시
public interface User{ ... }
- default 메소드 추가된 이유
· 기존

· 문제발생
(0.1 → 0.2)로 버전업 해서 a3()메소드 생성됨
→ 가&나&다 모두 a3()메소드가 구현이 되어있지 않아 컴파일 에러

· 해결
default 메소드로 구현까지 가능해짐 → 가&나&다 모두 a3()메소드 사용 가능해짐

[예제] 로또 번호 생성기 만들기

인터페이스 구현
package com.example;
/*
1. 1~45까지 써있는 Ball을 로또 기계에 넣는다.
2. 로또 기계에 있는 Ball들을 섞는다.
3. 섞인 Ball중에서 6개를 꺼낸다.
*/
//구현 하는 코드 x 선언만
public interface LottoMachine {
//인터페이스가 가지는 변수들은 모두 public static
int MAX_BAlL_COUNT = 45; // public static int ... 와 동일
int RETURN_BALL_COUNT = 6;
//인터페이스의 메소드는 모두 public abstract
public void setBalls(Ball[] balls); //Ball[] Ball이 여러개를 받겠다. 45개
public void mix();// 자기가 가지고 있는 Ball들을 섞는다.
public Ball[] getBalls(); // 6개의 Ball을 반환한다.
}
메소드 구현
package com.example;
public class Ball {
private int number;
public Ball(int number){
this.number = number; //초기값을 넘겨서 필드 초기화
}
public int getNumber() {
return number;//값을 return
}
}
package com.example;
public class LottoMachineMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Ball b1 = new Ball(1);
// Ball b2 = new Ball(2);
// ....
// Ball b45 = new Ball(45);
//ball변수가 45개가 필요. Ball인스턴스를 45개 참조할 수 있는 배열이 만들어진다.
Ball[] balls = new Ball[45];
// balls[0] = new Ball(1);
// balls[1] = new Ball(2);
// ...
// balls[44] = new Ball(45);
for (int i=0; i<LottoMachine.MAX_BAlL_COUNT; i++){
balls[i] = new Ball(i+1);
}
//LottoMachine 인스턴스가 생성
LottoMachine lottoMachine = new LottoMachineImpl();
lottoMachine.setBalls(balls); //balls넣어줌
lottoMachine.mix(); //섞기
Ball[] result = lottoMachine.getBalls(); // 6개 return한거 저장
for (int i = 0; i< result.length; i++){ //6번
System.out.println(result[i].getNumber());
}
}
}
package com.example;
//인터페이스를 구현하게 되면 반드시 인터페이스가 가지고 있는 메소드를 오버라이딩 할 필요가 있다,
public class LottoMachineImpl implements LottoMachine{
private Ball[] balls;
@Override
public void setBalls(Ball[] balls) {
this.balls = balls;
}
//Math.random() --> 0.0 <= x <1.0
// 0.0 <= x < 45.0
// (int) 0 <= x < 45
@Override
public void mix() {
for (int i=0; i<10000; i++){
int x1 = (int)(Math.random() * LottoMachine.MAX_BAlL_COUNT);
int x2 = (int)(Math.random() * LottoMachine.MAX_BAlL_COUNT);
if (x1 != x2){
Ball tmp = balls[x1]; //값을 치환할 때는 같은 type의 임시변수가 필요
balls[x1] = balls[x2];
balls[x2] = tmp;
}
}
}
@Override
public Ball[] getBalls() {
Ball[] result = new Ball[LottoMachine.RETURN_BALL_COUNT]; //Ball 6개를 참조할 수 있는 배열
for (int i=0; i<LottoMachine.RETURN_BALL_COUNT; i++){
result[i] = balls[i];
}
return result;
}
}
→ 출력:

+ 원리
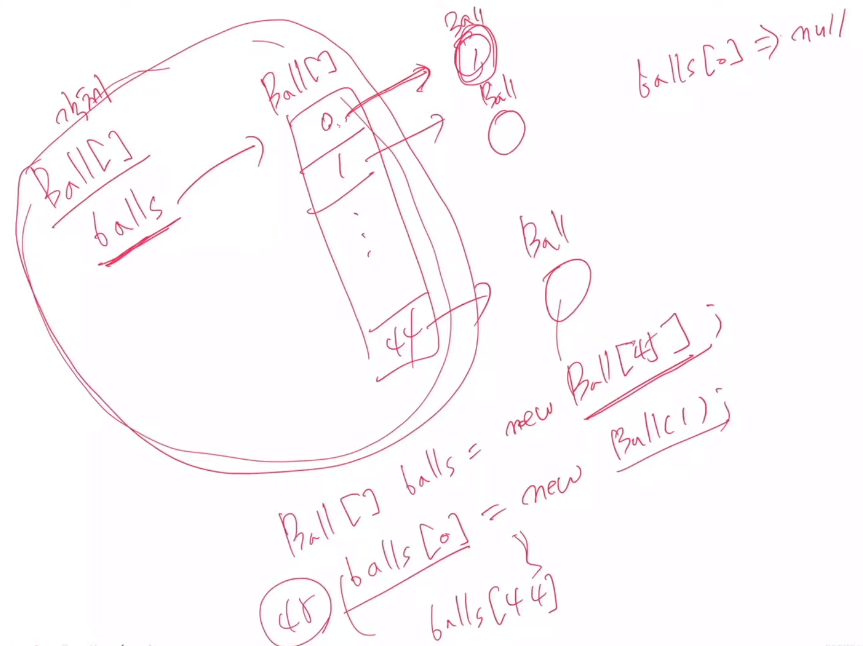
balls[0] => null이기 때문에 balls[0]~ balls[44]을 new ball(1)~ new ball(45)로 초기화 시킴

'[즐거운 자바 강좌] 정리' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [즐거운 자바 강좌] 섹션 5 - 배열(Array) (1) | 2024.03.31 |
|---|---|
| [즐거운 자바 강좌] 섹션4 - 팩토리 메소드(Factory Method) 패턴 (0) | 2024.03.31 |
| [즐거운 자바 강의] 섹션4 - 객체지향 문법 (3) (1) | 2024.03.31 |
| [즐거운 자바 강좌] 섹션3 - 객체지향문법(2) (0) | 2024.03.31 |
| [즐거운 자바 강좌] 섹션2 - 객체지향문법(1) (1) | 2024.03.31 |
